Frazer does Physics 3.2 Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
Grab the ends of the slinky in your hands. Stretch the slinky to between 1 and 2 meters long. Move your hands together and then apart, just as if you were clapping. Notice the motion of the slinky. Your hands move a lot while the center of the slinky moves very little. The center is a node.

Anatomy of a Transverse Wave? YouTube
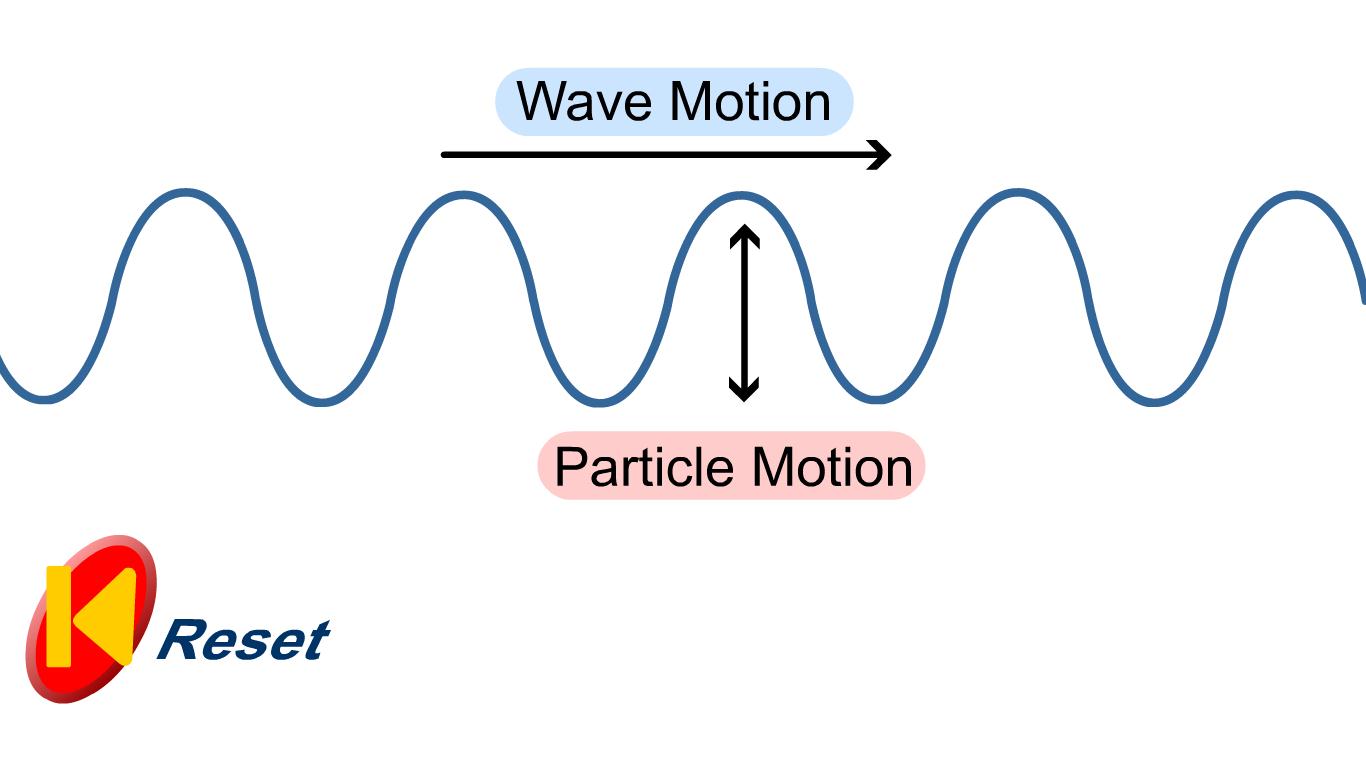
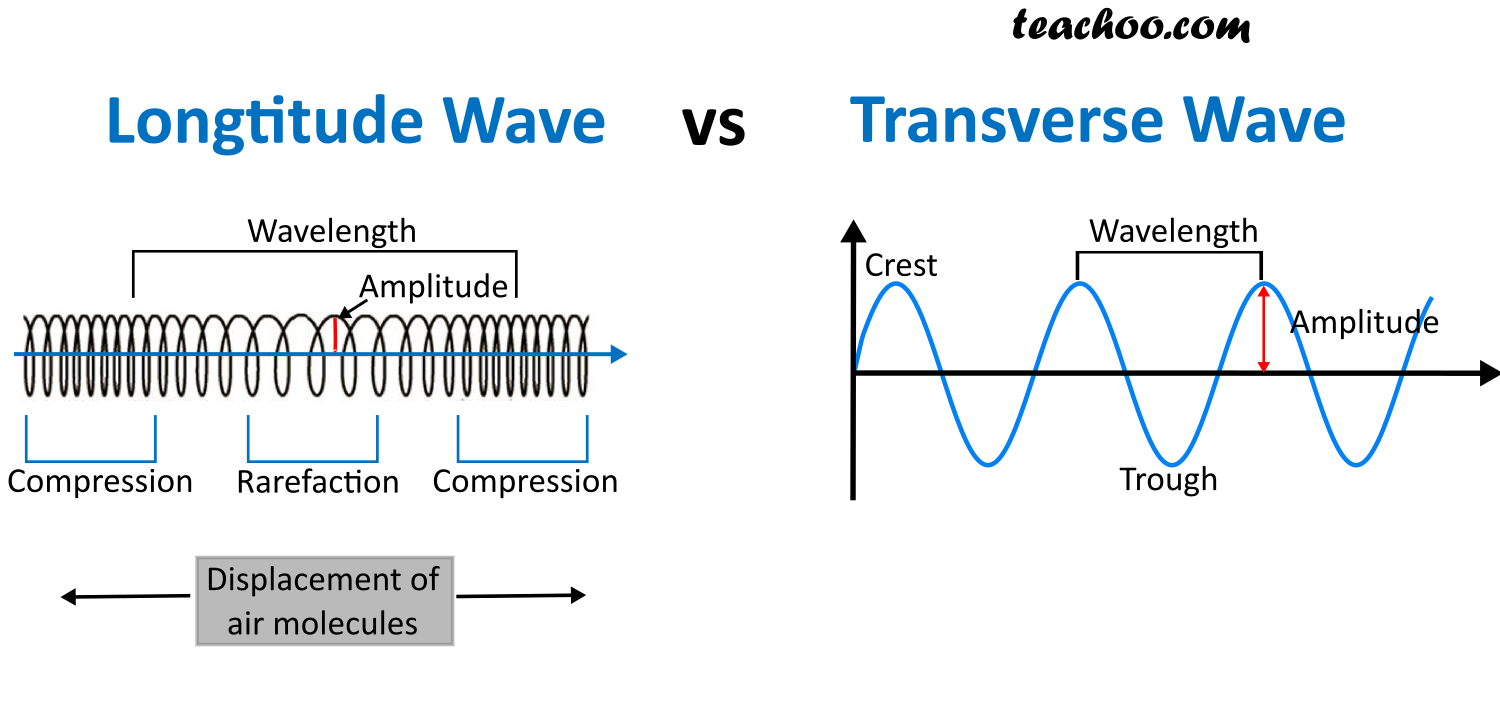
Speed at which the wave disturbance moves. Depends only on the properties of the medium. Also called the propagation speed. Transverse wave. Oscillations where particles are displaced perpendicular to the wave direction. Longitudinal wave. Oscillations where particles are displaced parallel to the wave direction.

Labeled Wave Diagram
Physics Waves Mechanical Waves Transverse Waves And Longitudinal Waves Transverse Waves and Longitudinal Waves In Physics, waves are explained as an oscillation about the fixed point, accompanied by the transfer of energy travelling from one medium to another.

Pin page
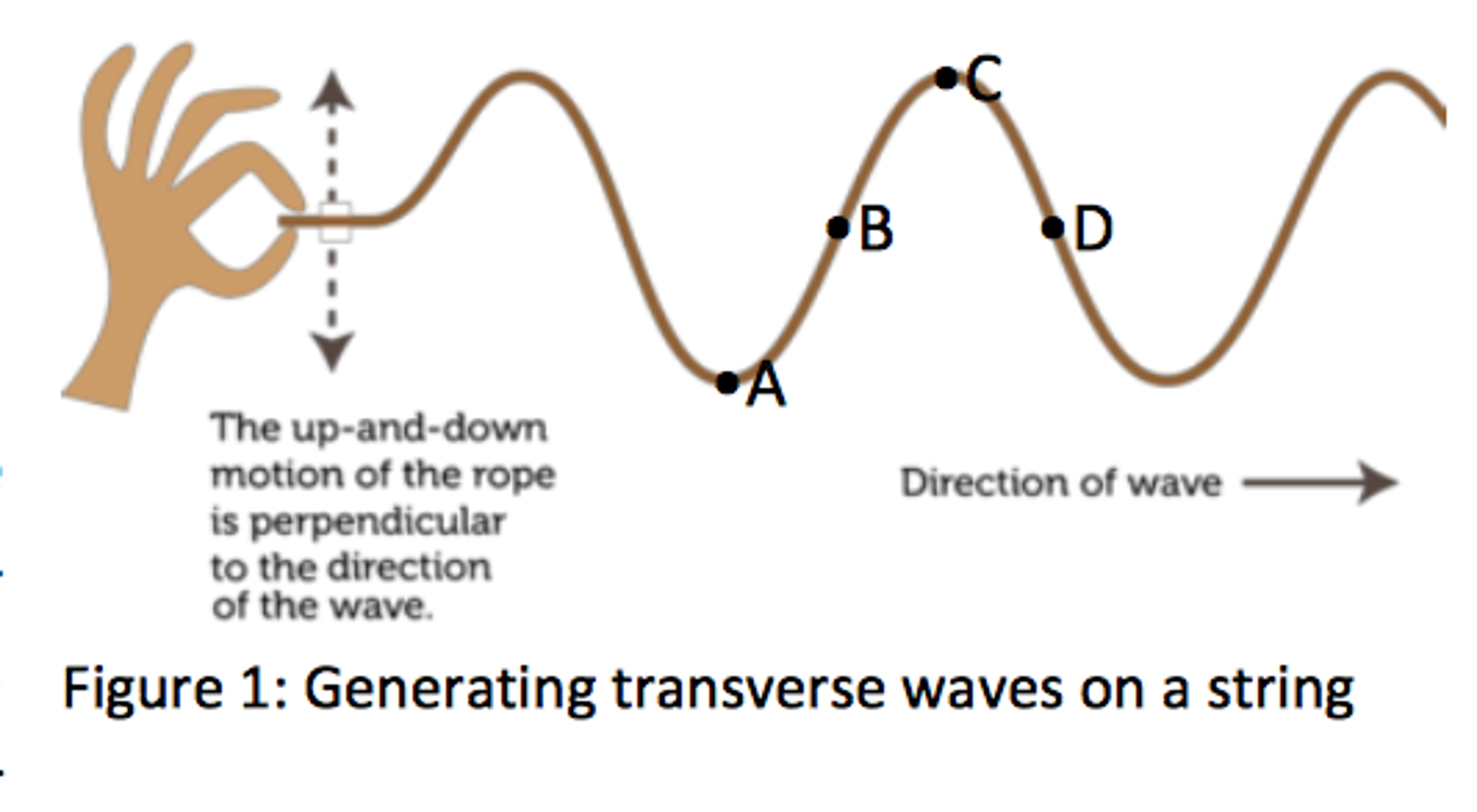
In Physics, a transverse wave is a moving wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave. A simple demonstration of the wave can be created on a horizontal length of the string by securing one end of the string and moving the other up and down.

Longitudinal and Transverse Labster
Category: Science & Tech Related Topics: shear wave transverse wave, motion in which all points on a wave oscillate along paths at right angles to the direction of the wave's advance. Surface ripples on water, seismic S (secondary) waves, and electromagnetic ( e.g., radio and light) waves are examples of transverse waves.

Transverse Wave Model YouTube
In physics, a transverse wave is a wave that oscillates perpendicularly to the direction of the wave's advance. In contrast, a longitudinal wave travels in the direction of its oscillations. All waves move energy from place to place without transporting the matter in the transmission medium if there is one.

Oscillations and Waves Transverse Waves a Simple Model YouTube
Objectives. Describe the nature of a wave as a disturbance that moves through a medium, transporting energy without transporting matter. Distinguish local particle vibrations from overall wave motion and relate these distinctions to types of waves such as longitudinal, transverse and surface waves. Demonstrate understanding of wave properties.
Binaural Beats Science How Do Binaural Beats Work?
In all types of mechanical waves, energy moves from one place to another while the media carrying the wave only vibrates back and forth in position. One type of mechanical wave is the transverse wave. In the case of transverse waves, the movement of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of the energy movement. Figure 11.2.2.

Transverse waves go across the plane and are perpendicular. Waves, Chart, Plane
In this activity, students explore the nature of waves using two models: one transverse and the other longitudinal. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students understand the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves. Teacher Tips
Difference between longitudinal and transverse waves Teachoo
You want to get the observation sheet for the video you watched - join Myunlab to get more resources https://unlab.thinktac.com.. When we see ripples in the.

Transverse Waves Sound waves, Longitudinal wave, Mechanical wave
Chemistry Bohr Model of the Atom Transverse waves. Key Questions. Question #a7b0f Answer: In material medium, transverse waves transfer energy due to the interactions that make up the medium. Electromagnetic radiation is a transverse wave due to how the magnetic and electric field interact with each other. Explanation:.

Which of the following is a transverse wave?
The forward speed of the wave is constant but the vertical speed of the material of the wave is not. Since velocity is the rate of change of position, the transverse velocity in the y y direction is given by the derivative of the displacement with respect to time: v(x, t) = ∂y(x, t)/∂t = −Aω cos(kx − ωt + ϕ) v ( x, t) = ∂ y ( x, t.
Solved (1) Regarding the transverse wave in Figure 1, what
GCSE AQA Synergy Waves - AQA Synergy Transverse waves Waves are one way in which energy may be transferred between stores. Both mechanical and electromagnetic waves will transfer energy.

Build Your Own Oscillating Wave Machine Physics projects, Steam projects middle school, Sound
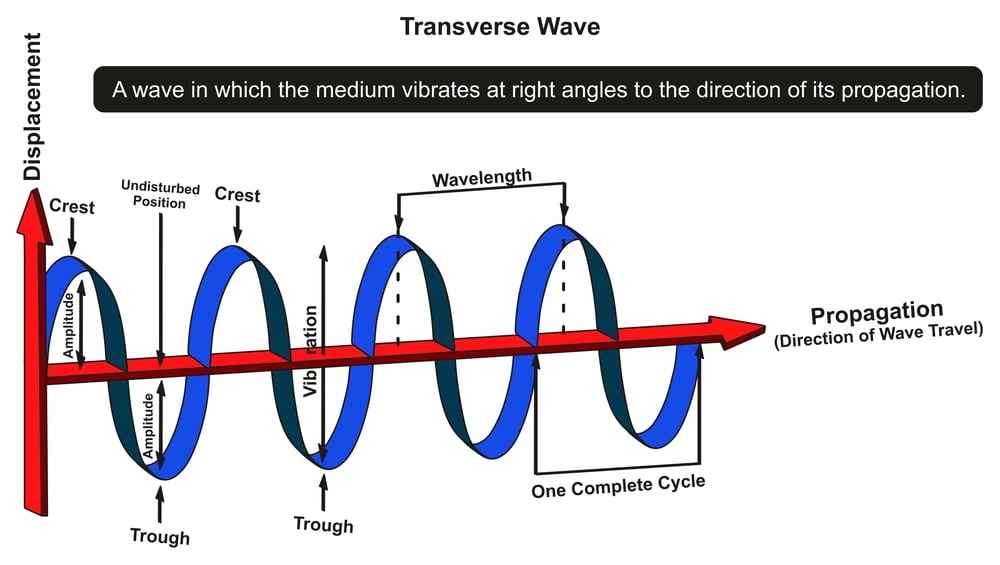
Tutorial 1.3: Transverse Waves. Transverse waves are the kind of wave you usually think of when you think of a wave. The motion of the material constituting the wave is up and down so that as the wave moves forward the material moves perpendicular (or transverse) to the direction the wave moves.Examples of transverse waves include waves on a string and electromagnetic waves.
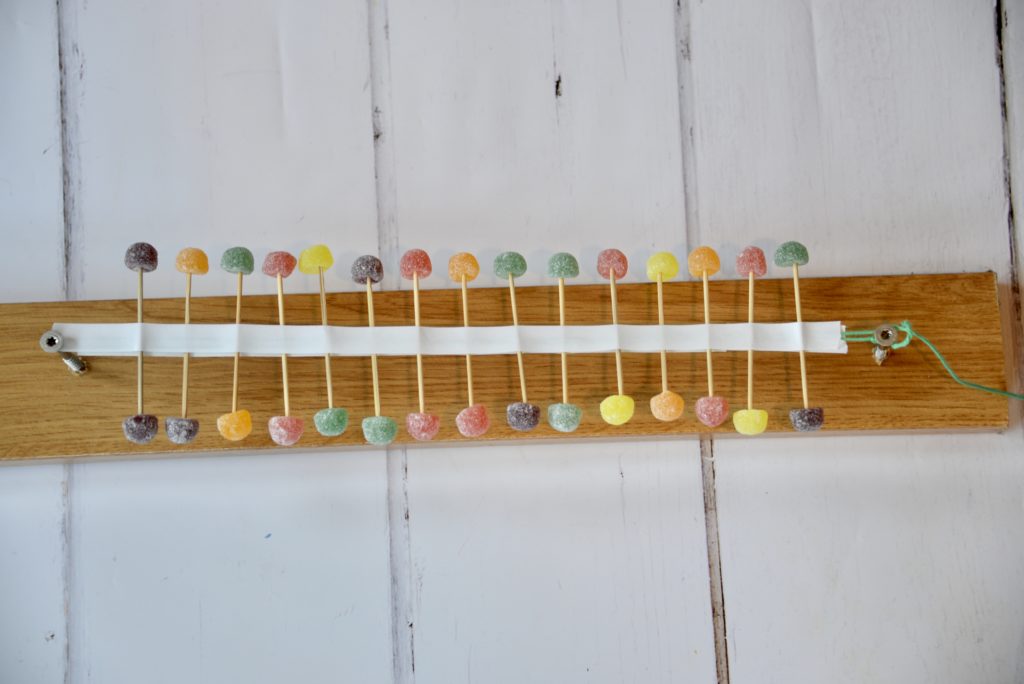

Mini Wave Machine
15:00 Video Transcript In this video, we're going to learn about modeling one-dimensional transverse waves. We'll see examples of these transverse waves. And we'll also see how to mathematically represent them.

Transverse vs Longitudinal Wave Leverage Edu
A transverse wave propagates so that the disturbance is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. An example of a transverse wave is shown in Figure 13.3, where a woman moves a toy spring up and down, generating waves that propagate away from herself in the horizontal direction while disturbing the toy spring in the vertical direction.